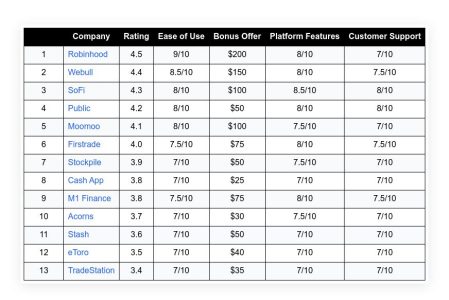
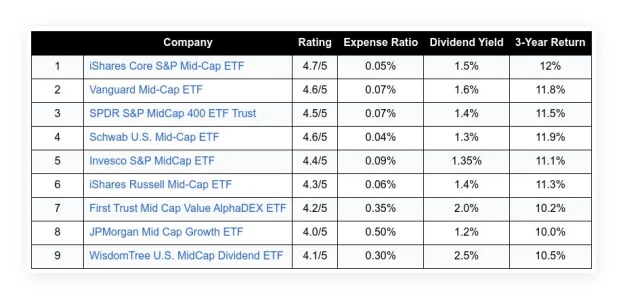
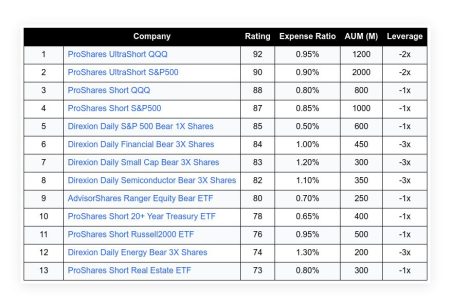
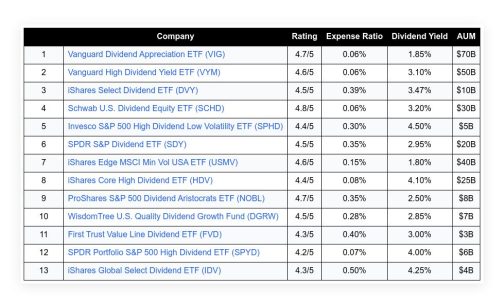
The financial market is a complex system influenced by a myriad of factors. One of the most significant factors that impact the market is inflation. Recently, the market has been experiencing some turbulence due to unexpected changes in inflation rates. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the current market situation, the role of inflation, and its impact on the Federal Reserve’s policies and the stock market.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding inflation
Inflation is a crucial economic indicator that measures the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising. The Consumer Price Index (CPI), a widely used measure of inflation, recently indicated that inflation is not decreasing to the anticipated 2% target. Instead, it has reaccelerated to three and a half percent. This figure is not alarmingly high, considering it was at 9% two years ago. However, the concern lies not in the absolute value but in the deviation from the expected trend.
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Taylor Sohns – CFP®, CIMA®, MBA – Finance (@lifegoalinvestments)
The market’s reaction to inflation
The market operates on expectations. When inflation was expected to continue its downward trajectory, the market adjusted accordingly. However, the recent flattening and subsequent reacceleration of inflation have taken the market by surprise. This unexpected change has caused a ripple effect, leading to market instability.
Inflation’s impact on Federal Reserve policies
The impact of inflation is not limited to the market alone. It also has significant implications for the Federal Reserve’s policies. Six months ago, when inflation was expected to continue downward, the Federal Reserve announced that it would begin cutting rates in 2024. This decision was based on the assumption that a lower inflation rate would allow for a more relaxed monetary policy. The stock market responded positively to this announcement, rallying 25% since that day.
Recent surge in inflation
However, the recent surge in inflation has thrown a wrench in these plans. Inflation has proven to be more persistent than anticipated, surprising the market and the Federal Reserve. At their last meeting, the Federal Reserve indicated that three interest rate cuts were likely. However, unless there is a dramatic change in the inflation trend, they will not be cutting rates this year.
The complex relationship between inflation, interest rates, and the stock market
The relationship between inflation, interest rates, and the stock market is complex. When inflation is high, the Federal Reserve typically raises interest rates to slow down the economy and bring inflation back to its target level. Higher interest rates, in turn, can make borrowing more expensive, potentially slowing economic growth and negatively impacting the stock market. Conversely, when inflation is low, the Federal Reserve can cut interest rates to stimulate economic growth, which can boost the stock market.
The current scenario
In the current scenario, the stock market has rallied 25% since the Federal Reserve announced rate cuts. However, the unexpected persistence of inflation has led to a change in the Federal Reserve’s stance. This change has the potential to negatively impact the stock market, as the anticipated rate cuts may no longer materialize.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the recent developments in the market highlight the importance of understanding the intricate dynamics between inflation, interest rates, and the stock market. The unexpected reacceleration of inflation has not only rocked the market but also led to a shift in the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy. As the situation continues to evolve, market participants will need to closely monitor these developments and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What is inflation and why is it significant?
Inflation is a crucial economic indicator that measures the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising. It is significant because it impacts the market and the Federal Reserve’s policies.
Q. How does the market react to inflation?
The market operates on expectations. When the trend of inflation was expected to continue its downward trajectory, the market adjusted accordingly. However, unexpected changes in inflation can cause market instability.
Q. How does inflation impact the Federal Reserve’s policies?
Inflation has significant implications for the Federal Reserve’s policies. For instance, when inflation was expected to continue its downward trend, the Federal Reserve announced that they would begin cutting rates. However, a surge in inflation can disrupt these plans.
Q. What is the relationship between inflation, interest rates, and the stock market?
When inflation is high, the Federal Reserve typically raises interest rates to slow down the economy and bring inflation back to its target level. Higher interest rates can make borrowing more expensive, potentially slowing down economic growth and negatively impacting the stock market. Conversely, when inflation is low, the Federal Reserve can cut interest rates to stimulate economic growth, which can boost the stock market.
Q. How has the recent surge in inflation affected the stock market?
The stock market has rallied 25% since the Federal Reserve’s announcement of rate cuts. However, the unexpected persistence of inflation has led to a change in the Federal Reserve’s stance. This change has the potential to impact the stock market negatively, as the anticipated rate cuts may no longer materialize.